Laparoscopic Surgery
Best in Delhi, India
Laparoscopic Surgery
There are two ways to do a surgery:
- Open, and
- Minimally Invasive
- Laparoscopic
- Robotic
Open Surgery
Traditional open surgery required a long incision on the abdomen, which resulted in delayed recovery, long hospital stays and bad scars.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Surgeons developed a novel approach to minimize suffering and improve outcomes. It is also called laparoscopic, minimally invasive or keyhole surgery. Laparoscopic surgery has transformed the field of gastrointestinal surgery. It is one of the most important innovation in the last few decades that has entirely changed the practice of surgery. It has now become a standard for many gastrointestinal operations. The advantages of laparoscopic surgery have been proven with research done across the globe.
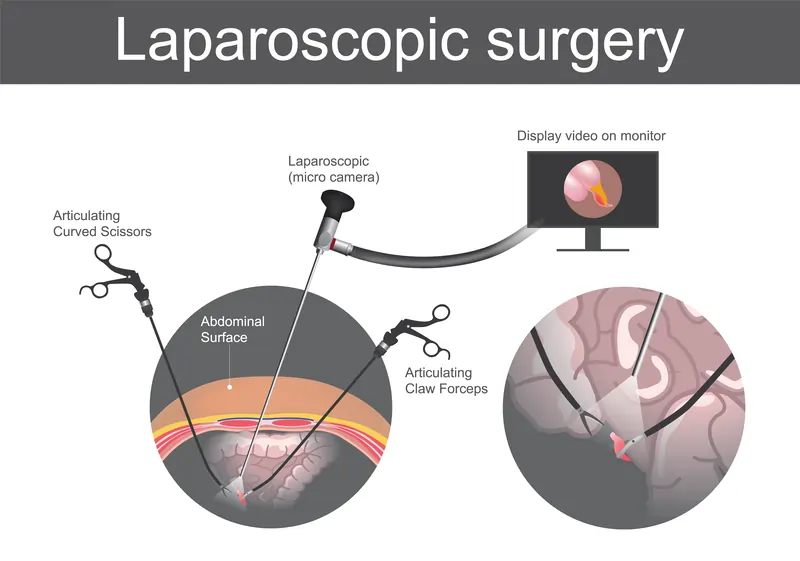
In laparoscopic surgery, few small holes called ports, are made over the abdomen. One of them is then used to insert a specially designed slender high-resolution camera. The camera projects a magnified view of the inside of the abdomen onto a high definition monitor. The rest of the ports are used for inserting specially designed long and thin instruments. The surgeon deftly maneuverers the instruments looking at the monitor and performs the surgery inside the abdomen. Thinking of a video game? But it's no child play, it requires intense training and practice.
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery combines the skill and expertise of a surgeon with the vision, precision, and flexibility of robotic technology. The robotic system features a 3D high-definition camera system for clear and enhanced vision with depth perception. It comprises a surgical console, where the surgeon sits, and robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments. The tiny wristed instruments can bend and rotate in ways the human hand cannot, allowing the surgeon to operate in tight spaces.
During robotic surgery, the surgeon makes minor cuts in the abdomen and inserts special tubes called ports. The robotic arms are connected to these ports, and the instruments mounted on these robotic arms go through the ports to do the surgery. A slender camera is also inserted through one port to show the surgeon a clear view of the inside. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console nearby, and an assistant helps by changing the instruments and aiding as needed.
Laparoscopic Liver Surgery
Liver resection or hepatectomy is a procedure in which a part of the liver is removed. It is done for tumour, cysts and cancer of the liver. It usually required a long incision over the abdomen. Laparoscopic liver resection is a minimally invasive approach to liver resections. With this, instead of a large incision, removal of part of the liver is accomplished with small holes over the abdomen. It gives all the advantages of laparoscopic surgery.
Liver resection has always been a challenging surgery. Special pieces of equipment are required to do the surgery laparoscopically. Your surgeon also needs to go through extensive training to perform this procedure safely. The risks associated with laparoscopic liver resection are the same as open liver resection.
Not all liver resections are suitable for a laparoscopic approach. Many resections are too complex to be performed laparoscopically. It is better to prefer an open approach in such cases.
Laparoscopic Choledochal Cyst Excision
The liver produces bile to help digest food. The bile duct is a tube that transports bile from the liver to the gall bladder and small intestine. A choledochal cyst (bile duct cyst) is an inborn anomaly of the bile duct. When a patient has a choledochal cyst, swelling of the bile duct occurs. This can cause liver problems or inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Patient with choledochal cysts has a higher rate of cancer of the bile duct in adulthood. Early surgery of choledochal cyst can reduce these risks.
Laparoscopic choledochal cyst excision is done through small incisions using miniaturized surgical tools and cameras or telescopes. Following excision of the bile duct, the small intestine is joined to the cut end of the remnant bile duct. This requires special skills to do it laparoscopically. The advantages of minimally invasive choledochal cyst excision include lesser pain, faster recovery, minimal scar and less risk of hernia formation.
Laparoscopic Stomach Cancer Surgery
Stomach cancer is treated with radical gastrectomy. In this procedure, part or whole of the stomach is cut with a healthy margin and all the draining lymph nodes. It is usually done with an open incision. Early cases of stomach cancer can now be operated on with a laparoscopic approach. It is important that as with an open approach, margin and lymph nodes are adequately cleared. The laparoscopic approach gives the advantage of a magnified view. The benefits of laparoscopic surgery are the same.
Laparoscopic Colon and Rectal Surgery
The surgical procedure for colon cancer and rectal cancer surgery is broadly called partial colectomy or rectal resection. It has various names depending on the segment of colon and rectum resected; right hemicolectomy, left hemicolectomy, sigmoidectomy, transverse colectomy, extended right or left hemicolectomy, anterior resection. low anterior resection and abdominoperineal resection. The technique of laparoscopic surgery allows surgeons to perform colon and rectal surgeries through small incisions. Laparoscopic colorectal surgery is now the standard of care for colorectal cancer treatment. It has now been adopted worldwide. It is important that as with an open approach, margin and lymph nodes are adequately cleared.
Thoracoscopic Oesophagectomy
The surgical procedure to remove oesophageal cancer is called oesophagectomy. Oesophagectomy is a surgical procedure that required opening up of both the chest and abdomen. With this, the recovery times were longer and complication rates were high. The term laparoscopic surgery is used for minimally invasive surgery of the abdomen. For thorax (chest), it is called thoracoscopic surgery. There have been substantial advances in laparoscopic and thoracoscopic equipment, skills, and techniques over the last decade. Oesophagectomy can now be done with minimally invasive techniques called thoracoscopic oesophagectomy. The abdominal part of the surgery is also performed laparoscopically, together called the thoraco-laparoscopic approach.
Laparoscopic Pancreatic Surgery
Cancer, tumour and cysts of the pancreas require surgical excision. Those in the head of the pancreas are removed with a surgical procedure called Whipple procedure or pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surgery to remove lesions in the tail and body of the pancreas is distal pancreatectomy. Distal pancreatectomy is more amenable to laparoscopic approach and is routinely done for smaller tumours. The Laparoscopic Whipple procedure is still in the developmental stage. It is done in select patients.
Laparoscopic Fundoplication
“Heartburn” is used to describe a variety of digestive problems. However, it is commonly a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease. In this condition, stomach acids reflux or “back up” from the stomach into the oesophagus. This irritated the lining of the oesophagus causing ulcers and various symptoms.
The most commonly performed operation for GERD is called a fundoplication. A fundoplication involves fixing your hiatal hernia, if present, and wrapping the top part of the stomach around the end of the oesophagus to reinforce the lower oesophagal sphincter. It thus recreates the “one-way valve” that is meant to prevent acid reflux. This procedure is now routinely done by minimally invasive techniques using several small incisions, called laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy
Achalasia cardia is a condition in which the junction (GE; gastroesophageal) of the oesophagus (food pipe) and stomach is too tight and does not relax for the food to pass through. It causes difficulty in swallowing liquid and solid food.
Laparoscopic Heller myotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that opens the tight lower oesophagal sphincter (the valve between the oesophagus and the stomach). It does so by performing a myotomy (cutting the thick muscle of the lower part of the oesophagus and the upper part of the stomach). This relieves dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
Minimally Invasive Necrosectomy for Pancreatitis
Pancreatic necrosectomy is the surgical procedure used in the management of acute pancreatitis, a condition characterised by the inflammation of the pancreas.
Pancreatic necrosectomy is traditionally performed via open surgery with an abdominal incision. In minimally invasive necrosectomy, dead parts of the pancreas and pus collection are accessed through small holes.
The ultimate goal of necrosectomy is to remove all the areas of infection and necrosis. Using forceps, the necrotic pancreatic tissues and debris are removed. Dissection should be limited to areas with loose tissues, making sure that normal pancreatic tissue is preserved.
Following the procedure, drains are inserted from the pancreatic area to minimise the exposure of the abdominal contents to the pancreatic juice.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery is beneficial for the patient in several ways. A long cut in the abdomen is no longer required. Post-operative stress and pain are markedly reduced, leading to a faster recovery and shortened hospital/ICU stay The amount of blood loss in the process of surgery has decreased. There is a quicker return of intestinal movement which is lost for some time after an open abdominal operation. The overall complication rate is decreased. All this results in an earlier return to home and work. The absence of a long scar is pleasant to the eyes.
The advantages of Minimally Invasive Approach:
- Less blood loss
- Less postoperative pain
- Reduced need for pain killers
- Faster healing time
- Shorter hospital stay
- Shorter ICU stay
- Early mobilization
- Quicker return of bowel function
- Earlier oral intake
- Quicker return to normal activity
- A faster return to work
- Lesser risk of infection
- Less risk of hernia formation
- Improved cosmetic results
- Improved quality of life
Stay Alert! Stay Healthy!
Wish you a speedy recovery!


